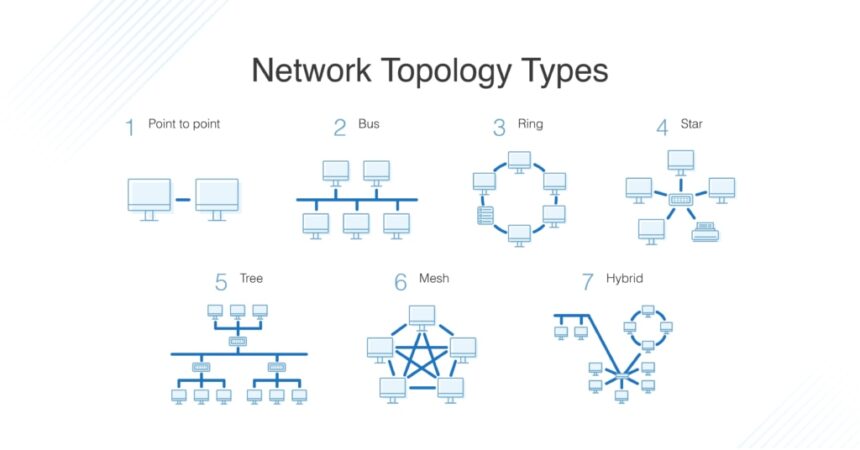
What is a network topology.
Topology is the physical and logical arrangement of a local area network. The physical topology of a network refers to the physical arrangement of cables, computers, and other peripheral devices in relation to each other on a network meanwhile Logical topology is the method used to pass information between workstations on a network.
Types of physical network topologies
- Bus network topology
- Ring network topology
- Star network topology
- Hierarchical network topology
- Mesh network topology
- Hybrid topology
- Tree topology
- Point-to-Point
Bus topology or linear bus topology
Bus network topology is one that consists of a main, central cable known as the backbone with a terminator at each end of it where all devices on the network are connected to the main/central cable.
Advantages of Bus topology
It is less expensive than a star topology due to less footage of cabling, only needs one main cable and no network hubs
It is good for smaller networks not requiring higher speeds
It has a high transmission speed if coaxial cable is used.
It is easy to add new workstations on the net work.
Multiple servers can be used.
Easy to connect a computer or peripheral to a bus.
Requires less cable length than a star topology.
Failure of one device doesn‘t affect others.
Disadvantages of Bus network
It is Limited in size and speed
The Entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable.
Difficult to troubleshoot. it is difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down
It is less secure since all data is transmitted down one main cable.
Transmission slows down as more work stations are added.
If the main cable fails, then all workstations are affected.
Ring topology
This is a topology where all devices on the network are connected to one another in the shape of a closed ring or a loop to form a ring. Data travels in form of a packet from one device to another device around the entire ring in only one direction until it reaches its final destination.
In a ring topology, there are nodes and the work of these nodes is examined any data that passes by to see if it is the address; if not, the data is passed on to the next node in the ring.
Advantages of ring topology
It is a Very orderly network where every device has access to the token and the opportunity to transmit
It performs better than a star topology under heavy network load
Can create much larger network using Token Ring
It is Cheaper to install than star network as there is only one cable between each workstation.
High speed can be achieved as each workstation can boast the signal.
Disadvantages of a Ring network
One malfunctioning workstation or bad port in the central hub can create problems for the entire network
Moves, additions and changes of devices affect the entire network.
Network adapter cards are expensive.
It is much slower than an Ethernet network under normal load
Less secure than star network as data pass through a number of workstations before reaching its destination.
Star topology
A star topology is a type of topology designed where computers and other devices are connected directly to a central network hub or switch thus forming star.
Data on a star network passes through the hub or switch before continuing to its destination. The hub or switch manages and controls all functions of the network.
Extended Star topology
This is a network where more than one individual’s star topologies are connected together. At the center of the star is a hub or a switch. It extends the length and size of the network.
Advantages of Star /extended star topologies
It is suited for large networks
It is easy to expand the network without any negative effects
If one cable or station fails, the entire network is not affected
It is easy to install, maintain and troubleshoot because the problem usually isolates itself.
Different types of cables can be used to maximize efficiency.
High speed transmission is possible since each station has a dedicated cable.
Greater security as connection from one station to server is unique.
No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices.
Disadvantages of Star/extended star topologies
Breakdown of the switch/Hub becomes a single point of network failure
It’s expensive to set up due to increased cabling costs and the need for a switch or hub.
Mass of cables are needed around in case of a large network.
If the cable fails the workstation cannot receive data via any other route.
The server can get congested as all communication must pass through it
Requires more cable length than a bus topology.
If the hub or switch fails, nodes attached are disabled.
Hierarchical topology
This is a type of topology that resembles extended star topology, except that computer controls traffic instead of a hub or a switch.
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology is combination of two or more different topologies (bus, star, ring, etc.). The hybrid network is based on both peer-to-peer and client-server relationship.
A hybrid topology is easier to connect to other computers than some other topologies. Also the hybrid topology has a faster connection.
Advantages of hybrid topology
• Very reliable and easy to detect the faulty system.
• It is easy to troubleshoot.
• It includes both wired and wireless network.
• It is expandable network.
Disadvantages of hybrid topology
• Its design is difficult to understand.
• The cost of this network design is high, because of requirement of lot of cables, cooling systems, etc.
• MAU (Multi-station Access Unit) is required.
• It is expensive to install and maintain
Tree topology
A tree topology is a type of network topology that has combined characteristics of bus and star topologies; it consists of groups of star-configured workstations connected to a bus backbone cable.
Tree topologies allow for the expansion of an existing network, and enable organizations to configure a network to meet their needs. It can be used to connect a bus network in buildings onto star topologies in different buildings.
Advantages of Tree topology
Allows for Point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
Expansion of Network is possible and easy.
It is easy to manage and maintain because the network is divided into segment
Error detection and correction is easy.
If one segment is damaged, other segments are not affected
Disadvantages Tree topology
Overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used.
If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down.
More difficult to configure and wire than other topologies.
Difficult to troubleshoot problem.
This network is not secure, anyone can see transmitted data.
As more and more nodes and segments are added, the maintenance becomes difficult.
Mesh topology
This is a network where each device has its own connections to all other devices on the network. It provides each device with a point-to-point connection to every other device in the network. Data sent on a mesh network can take any of the several paths from the source to the destination.
Advantages of Mesh topology
A mesh topology provides much protection from interruption of service because of possible routes through the network that is the damage of one or several cables or computers may not have vital impact except the involved computers
Mesh networks provide redundancy, in the event of a link failure; meshed networks enable data to be routed through any other site connected to the network.
Disadvantages Mesh topology
Much cabling is needed hence expensive
Not easy to troubleshoot incase of failure
Not easy to install.
It is the most expensive and difficult to maintain topology because each device has a point-to-point connection to every other device.
The damage of at least one cable or device may damage the network seriously If there are only few cables in the network
Point-to-Point Topology
Point-to-point (PTP) topology is a type of topology that connects two nodes directly together.
The following examples are pure point to point links:
Two computers communicating via modems.
A mainframe terminal communicating with a front end processor.
A workstation communicating along a parallel cable to a printer.